Video formats and file sizes are often confusing for most people. When you watch a video, you rarely notice any difference between formats like MP4, AVI, or MKV. Yet, the moment you try to share or upload a video, format compatibility becomes a critical factor.
On the other hand, video size can be equally perplexing—how can a high-resolution video sometimes be smaller than one shot on your iPhone? These inconsistencies make it challenging to understand what actually affects video size and format.
This blog will clarify the relationship between video formats and codecs, explaining their roles in video quality, compatibility, and file size. By the end, you’ll have a clearer picture of what matters most when optimizing videos for storage, sharing, or streaming
Video format has minimal impact on compression size.
I know the conclusion above sound strange enough but I will try to explain what are all these concepts about. Please read on!
What Exactly is Video Format?
At first glance, video formats like MP4 or AVI may seem straightforward—you might recognize them as the file extensions on your videos. But what exactly is MP4, and how is it different from AVI? Why do we need multiple formats? To understand this, we need to dive into what a video format actually is and its role in video files.
Video Format: The Container
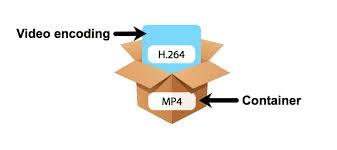
A video format is essentially a container for the actual encoded video images and audio. Think of it as a package that binds a silent video with its corresponding audio, along with additional information. For instance, an MP4 file is structured with three main components:
- Video: The encoded visual content, often compressed using a specific codec.
- Audio: The corresponding sound, also encoded separately.
- Metadata: Supporting information like time alignment between video and audio, subtitles, file descriptions, and more.
Differences Between Formats: Mostly Metadata Parts
The primary distinction between video formats, such as MP4 and AVI, lies in the way metadata is handled and the codecs they support. This metadata determines how the video and audio are synchronized and displayed, but it has minimal impact on file size. In fact, converting a video from one format to another will rarely change the file size significantly because the bulk of the size comes from the encoded video and audio data within the container.
Why So Many Formats?
The abundance of video formats stems from different industry standards and the competing needs of technology companies over time. For example:
- AVI: One of the earliest formats, developed by Microsoft in the early 1990s, was widely used for compatibility with Windows.
- MOV: Introduced by Apple, this format became standard for macOS and iOS ecosystems.
- MP4: Based on an open standard, it quickly gained popularity for its versatility, efficiency, and cross-platform support.
Over time, MP4 has become the most widely supported and used format, thanks to its balance of compatibility, compression efficiency, and ability to handle rich metadata. This ubiquity makes it the go-to choice for everything from streaming to file sharing.
What Determines the Size of a Video Then?
While the video format acts as the container, the factors that truly determine the size of a video are the way its content is encoded and compressed. Three main elements come into play:
1. Video Codec
A video codec is the technology used to compress and decompress the visual data in a video. It is responsible for reducing the size of raw video footage by identifying and removing redundancies without (ideally) compromising perceptible quality.
Popular codecs include:
- H.264 (AVC): The most widely used codec, known for its balance between compression efficiency and quality.
- H.265 (HEVC): A more advanced codec that offers up to 50% better compression than H.264 but requires more processing power.
- AV1: An emerging codec with excellent compression efficiency, aimed at reducing file sizes for streaming and storage.
The choice of codec significantly affects file size—modern codecs like H.265 and AV1 can create much smaller files compared to older codecs like MPEG-2 while maintaining similar quality.
2. Image Content and Resolution
The actual content of the video and its resolution play a major role in file size:
- Content Complexity: A video with fast-moving scenes or lots of detail (e.g., an action movie) requires more data to encode compared to static or low-motion scenes (e.g., a talking head).
- Resolution: Higher resolutions (e.g., 4K) have more pixels to encode, which directly increases file size. For example, a 4K video will typically be much larger than a 1080p version of the same content.
3. Coding Method:
- Bitrate: The amount of data used to encode one second of video. Higher bitrates result in better quality but larger files.
- Constant Bitrate (CBR): Uses a fixed data rate, which can waste storage for simple scenes.
- Variable Bitrate (VBR): Adjusts the data rate dynamically based on scene complexity, leading to better compression efficiency.
- Frame Rate: The number of frames per second (e.g., 30fps or 60fps). Higher frame rates improve smoothness but also increase file size.
- Compression Techniques: Advanced methods, such as predictive encoding, analyze and store only the differences between frames, significantly reducing file size.
You can learn about why those matters in this blog about how large a video should be
Try Redpandacompress to Compress your video
Compressing videos can feel overwhelming with so many technical aspects to consider—formats, codecs, resolution, and more. That’s where Redpandacompress.com steps in, making the process simple and effective for everyone.
1. Use MP4 Format
MP4 is the most versatile and widely supported video format available today. Whether you’re sharing a video on social media, uploading to a cloud storage service, or playing it on various devices, MP4 ensures compatibility across platforms. Redpandacompress automatically saves your compressed videos in this reliable format, so you never have to worry about format conflicts.
2. Auto Compression for Optimal Size and Quality
Redpandacompress uses smart algorithms to determine the best size for your video without sacrificing quality. By analyzing your video’s content, codec, and resolution, it ensures the file is as small as possible while preserving its visual and audio integrity. Whether you need a high-quality video for streaming or a smaller file for quick sharing, Redpandacompress handles it all seamlessly.
With just a few clicks, you can take the guesswork out of video compression and enjoy optimized videos that are easy to share, store, and upload. Try Redpandacompress.com today and experience hassle-free video compression!